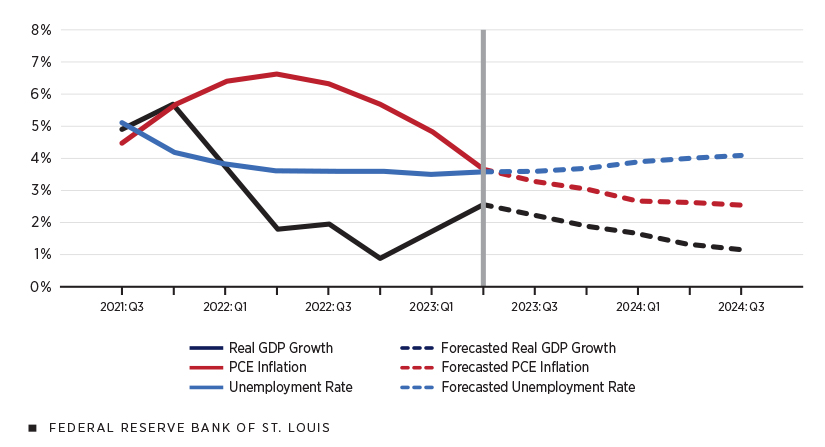
The U.S. economy exhibited robust growth, expanding at a 3.2% annual pace in the fourth quarter of 2023, as reported by the Commerce Department on Wednesday.
Although this figure represents a slight downgrade from the initial estimate of 3.3%, it underscores the nation’s economic resilience. The GDP’s total output of goods and services slipped from a red-hot 4.9% in the previous quarter, marking six consecutive quarters of growth exceeding 2%. This statistics is part of the second of the three estimates of the GDP growth.
Consumer Spending and Government Investments Drive Growth
Consumer spending, constituting approximately 70% of U.S. economic activity, grew at a solid 3% annual pace from October through December. Simultaneously, spending by state and local governments surged at a remarkable 5.4% annual rate, the fastest pace since 2019. The combination of robust consumer and government spending, along with growing exports, contributed to the overall economic expansion.
Inflation Pressures Easing
The report also highlighted a positive trend in easing inflation pressures. The Federal Reserve’s preferred measure of prices, the personal consumption expenditures price index, rose at a 1.8% annual rate in the fourth quarter, down from 2.6% in the third. Core inflation, excluding volatile food and energy prices, accelerated slightly from a 2% increase in the third quarter to 2.1% in the fourth.
2024 Outlook and IMF Forecast
The United States is expected to continue its growth trajectory in 2024, with the International Monetary Fund (IMF) forecasting a 2.1% expansion. This projection exceeds forecasts for growth in major advanced economies, including Japan, Germany, the United Kingdom, France, and Italy.
Economic Considerations Ahead of the Presidential Election
With the presidential election approaching in November, voters are scrutinizing the economy’s health. Despite concerns about high prices, attributed by some to President Joe Biden, inflation has eased, and hourly wage hikes have outpaced price increases over the past year. However, consumer prices remain 17% higher than three years ago.
Federal Reserve’s Response to Inflation
To counter resurgent inflation, the Federal Reserve raised its benchmark interest rate 11 times between March 2022 and July 2023, reaching the highest level in over two decades. This move successfully reined in the inflationary surge, with consumer prices rising just 3.1% from January 2023, down from a peak of 9.1% in June 2022.
The Unemployment Rate and Job Growth
Surprisingly, the progress against inflation has not led to significant economic pain. The unemployment rate has stayed below 4% for 24 consecutive months, the longest such streak since the 1960s. Employers have consistently added an average of 244,000 jobs per month over the past year, contributing to a healthy job market.
Hopes for a “Soft Landing”
The combination of easing inflation, steady job growth, and positive GDP trends has raised hopes for a rare economic phenomenon — a “soft landing.” This scenario envisions conquering inflation without triggering a recession. Rubeela Farooqi, Chief U.S. Economist at High Frequency Economics, expressed optimism about the economy’s future, predicting slowed but positive growth in the coming quarters. The Federal Reserve’s plan to cut its benchmark rate three times in 2024 is expected to provide additional support.
In conclusion, the U.S. economy’s performance in the fourth quarter of 2023 reflects resilience and sustained growth, with optimism for continued positive momentum in 2024. The challenges posed by inflation have been met with strategic Federal Reserve interventions, fostering economic stability as the nation navigates the path ahead.











